Software
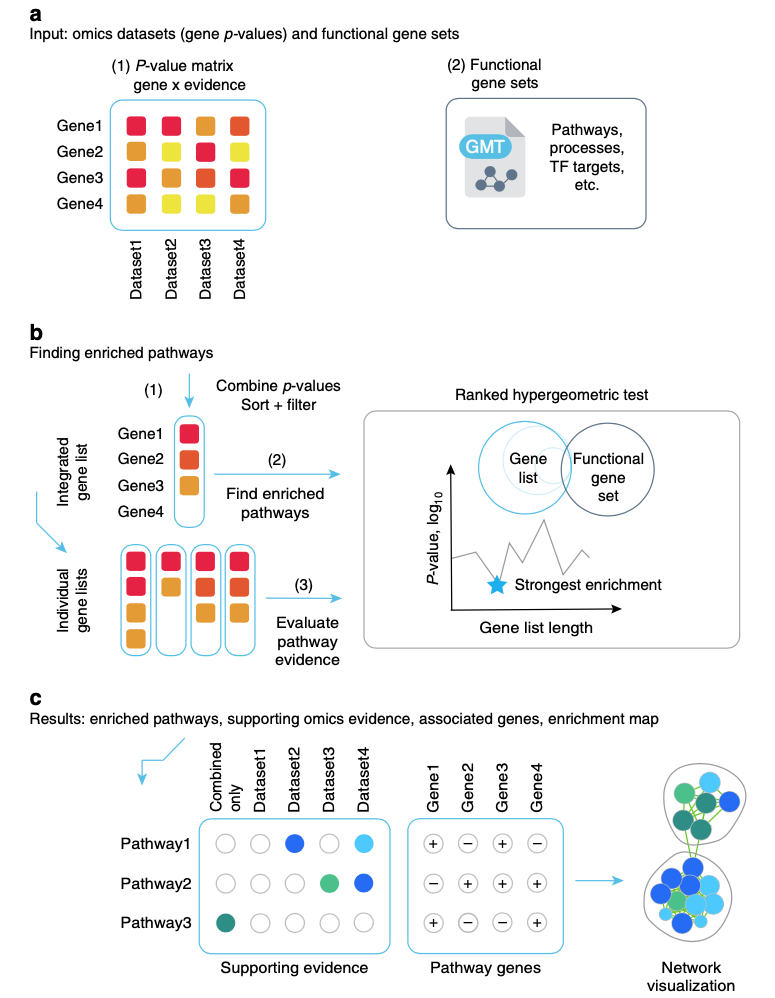
ActivePathways
ActivePathways is a method for integrative pathway enrichment analysis of multi-omics datasets. It uses a data fusion approach of P-value merging to prioritize genes and pathways in multiple complementary omics datasets and evaluates the omics evidence supporting each detected pathway and gene. It can be integrated easily with the EnrichmentMap app in Cytoscape to visualize enriched pathways and underlying evidence.
CRAN: R package.
GitHub: source code.
Paper: Paczkowska, Barenboim et al. Nature Comms 2020 (with the PCAWG project).
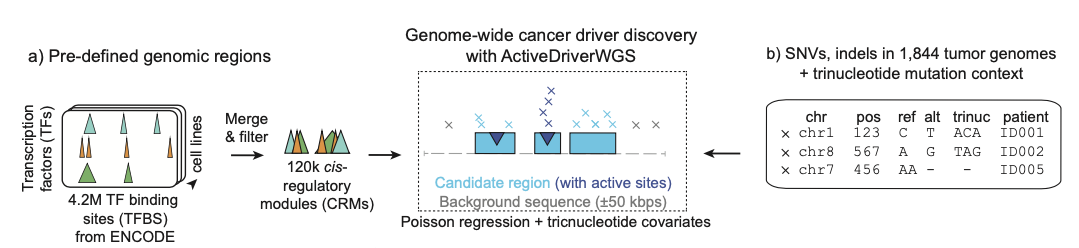
ActiveDriverWGS
ActiveDriverWGS is a method for discovering cancer driver mutations in genes and non-coding genomic elements. It uses Poisson regression to identify frequently mutated elements that are potentially positively selected in cancer genomes. The model uses local sequence adjacent to the region of interest to derive expected mutation frequencies and adjusts for trinucleotide sequence and mutation context for improved analysis.
CRAN: R package.
GitHub: source code.
Paper: Zhu, Uuskula-Reimand, Isaev et al. Molecular Cell 2020.
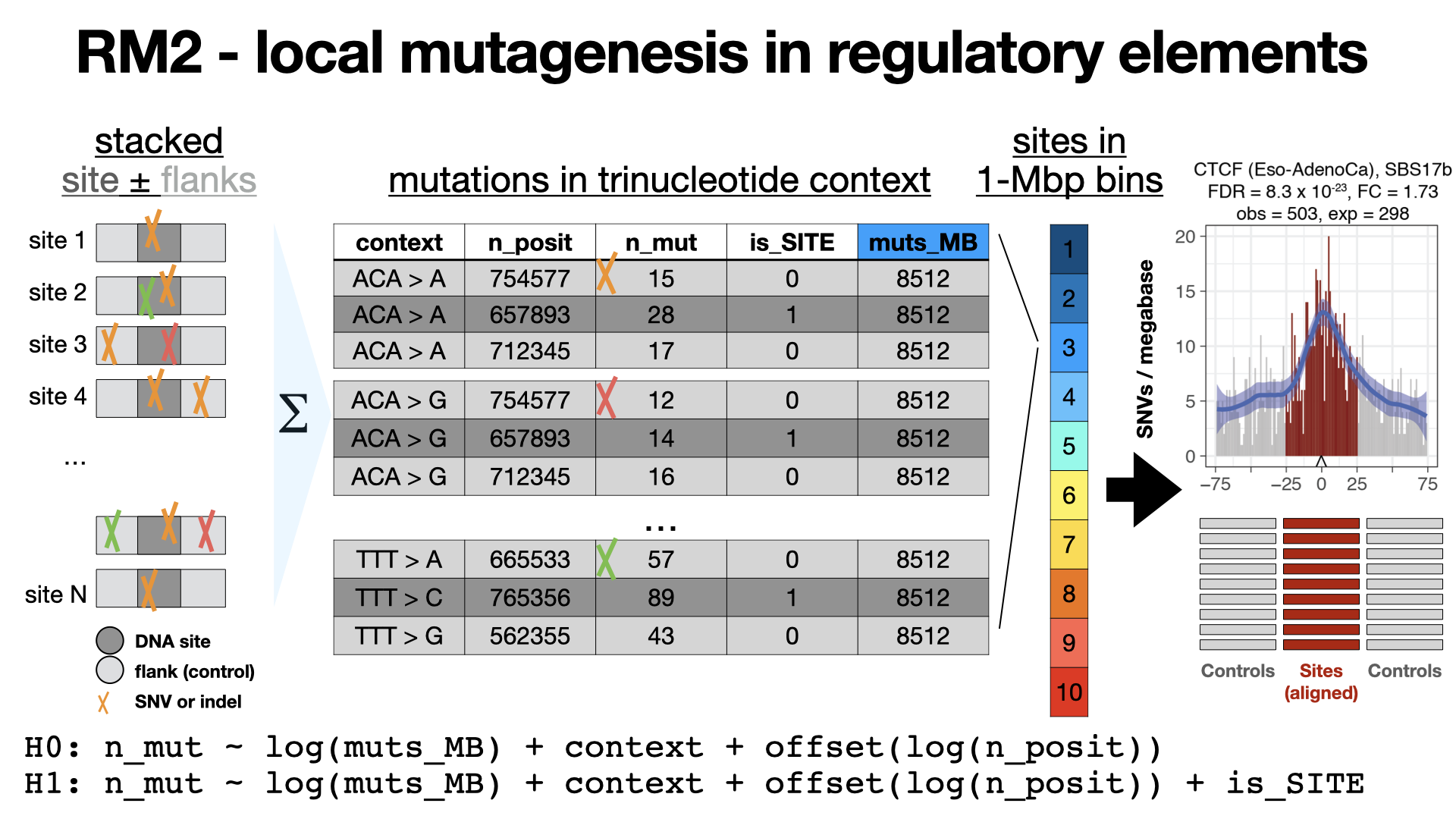
RM2
RM2 is a method to characterize local mutational processes acting on families of genomic elements in cancer genomes. The negative binomial regression model in RM2 evaluates the frequency of somatic mutations in such elements, relative to the background mutation rates in adjacent sequences and also adjusts megabase-scale mutation frequencies as covariates. Optionally, the analysis also considers clinical and genetic properties of the sequencing dataset to find their interactions with localized mutational processes.
GitHub: source code.
Paper: Lee, Abd-Rabbo, Reimand. Genome Biol 2021.
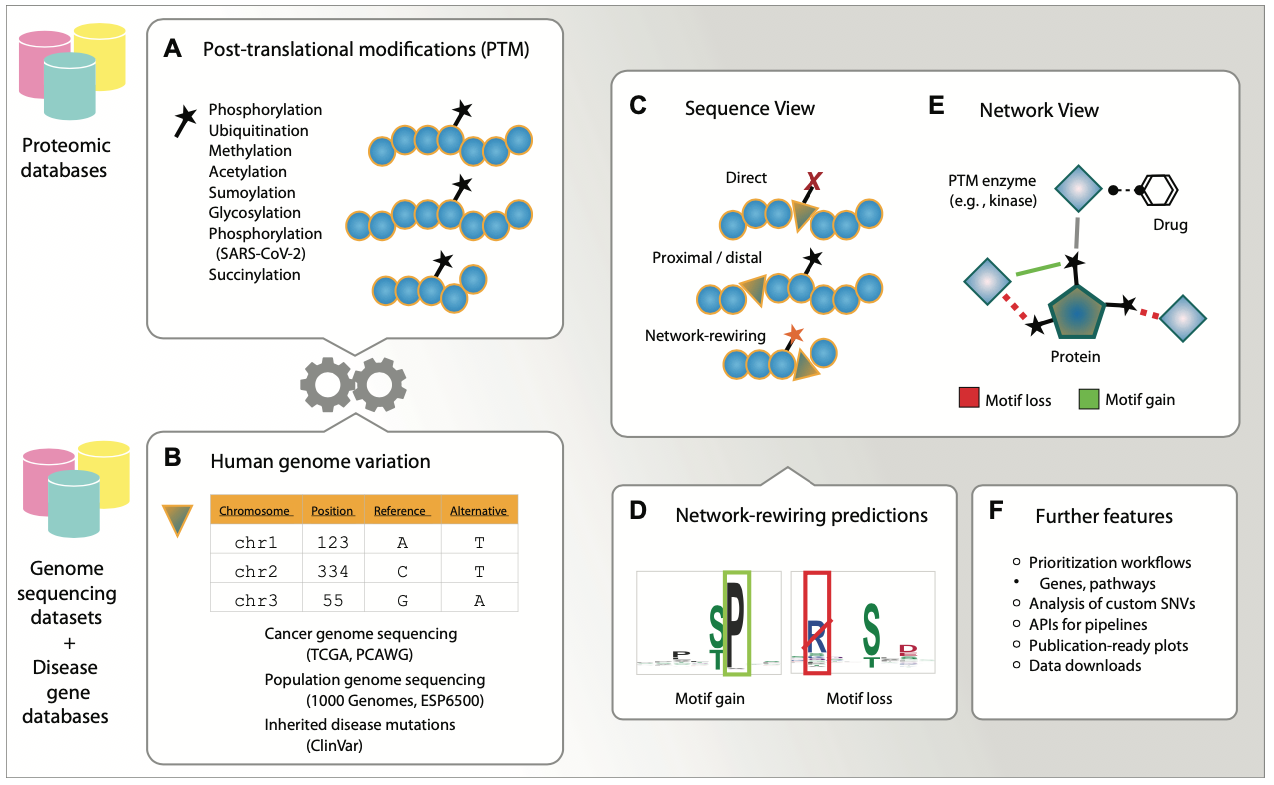
ActiveDriverDB
ActiveDriverDB is a database for interpreting human genomic variation using cell signalling networks. We analyze missense SNVs (amino acid substitutions) that occur at post-translational modification sites (PTM sites, such as phosphorylation). Somatic cancer mutations, inherited disease mutations, and polymorphic variations in the human genome are included. We evaluate the impact of substitutions on kinase signalling networks by predicting whether the substitutions alter protein sequence motifs bound by kinases and potentially cause rewiring of signalling networks.
Web server: www.activeDriverDB.org.
GitHub: source code.
Original paper: Krassowski et al. Nucleic Acids Res 2018.
2021 update paper: Krassowski et al. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021.