New preprint: Human phospho-signaling networks of SARS-CoV-2 infection are rewired by population genetic variants
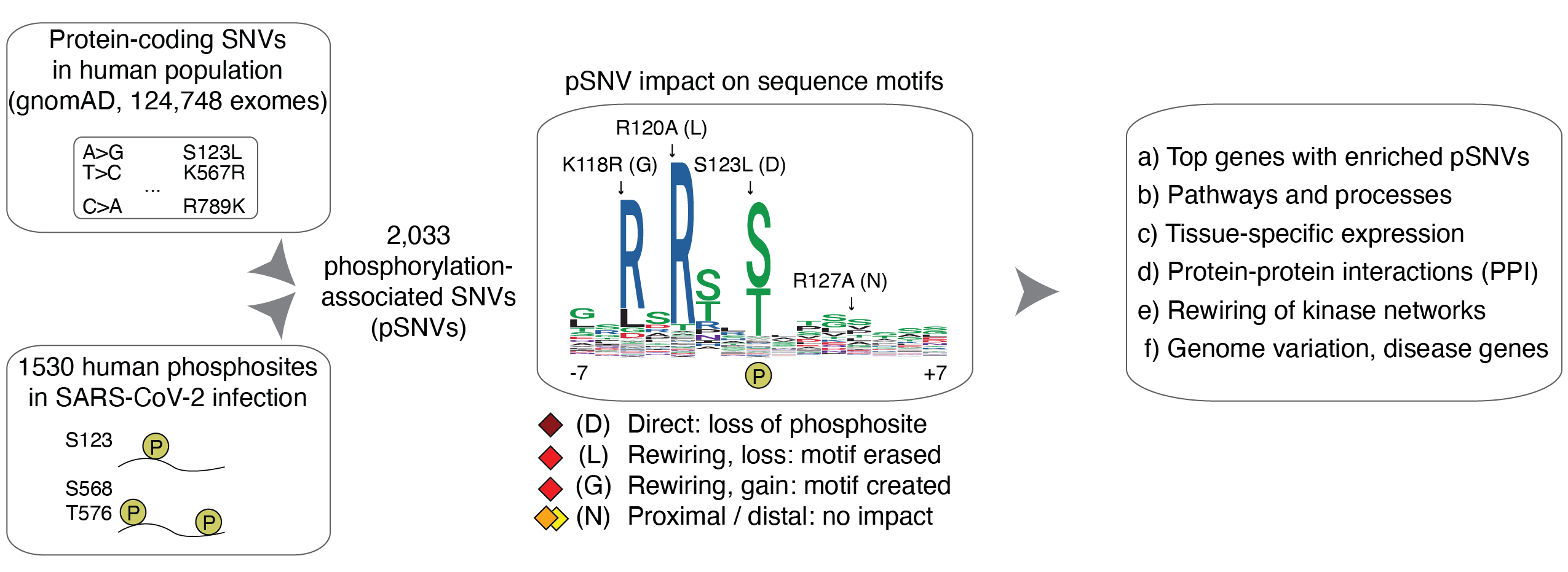
We posted a new preprint on medRxiv on our recent study of human genetic variation affecting the phosphorylation signalling networks of SARS-CoV-2 infection. We used a machine learning approach to identify protein-coding variants (SNVs, single nucleotide variants) in human population genomics data (gnomAD) that erase protein phosphorylation sites or modify short sequence motifs at the sites, potentially causing genetic rewiring of human signaling networks altered upon virus infection. The phosphorylation associated SNVs (pSNVs) are enriched in cellular pathways involved in virus life cycle, innate immune response, protein-protein interaction networks of host and virus proteins, as well as pathways involved in human comorbidities of COVID-19. The study was co-led by the postdoctoral fellow Diogo Pellegrina and PhD student Alec Bahcheli in our lab.